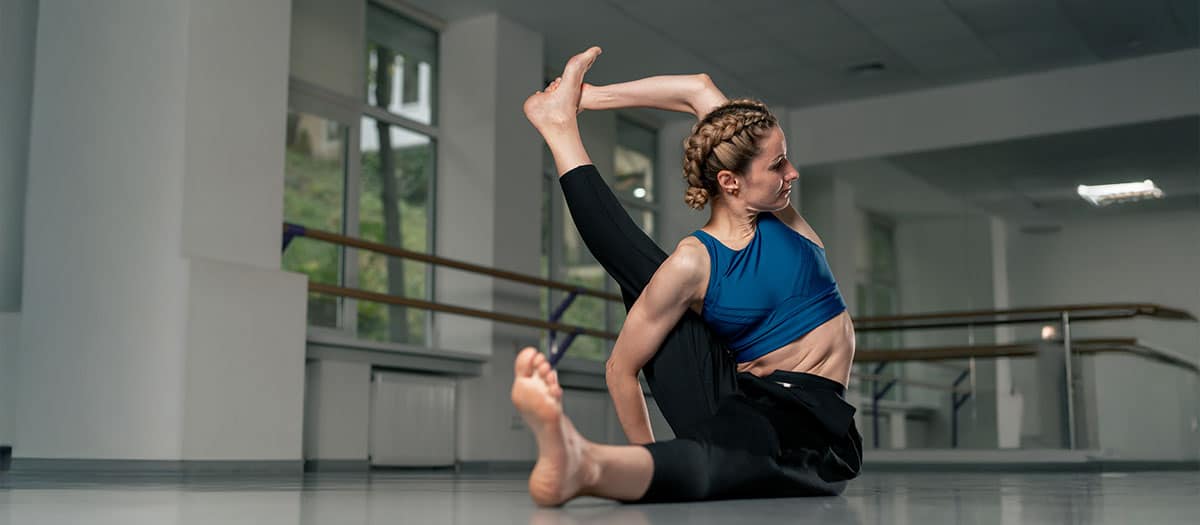
Joint hypermobility, while often seen as an advantage in activities like yoga, gymnastics, or dance, can cause significant challenges and pain for some individuals. In this article, we’ll explore what joint hypermobility and Hypermobility Spectrum Disorder (HSD) are, their effects on daily life, and how physical therapy can help.
What is Joint Hypermobility and Hypermobility Spectrum Disorder?
Joints are places where bones meet and allow for movement in the body, such as the knee or shoulder. Some people are born with greater joint motion than expected, and if this affects most of the body’s joints and causes pain or dysfunction, it may qualify as a disorder, known as Hypermobility Spectrum Disorder (HSD). HSD is a common body type, affecting women more often than men. This disorder may have genetic or hereditary components and can be a symptom of conditions such as Marfan syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, or Down syndrome. However, a person can present with hypermobility without these syndromes or a family history of the condition.
Common Symptoms and Challenges of Hypermobile Joints
How Does Joint Hypermobility Impact Daily Life and Physical Activity?
The Role of Physical Therapy in Managing Hypermobile Joints
Physical therapy can be an effective way to manage the symptoms of hypermobility. A physical therapist can assess whether tightness in the body is due to muscular tightness or joint stiffness and help individuals with HSD learn how to exercise safely. Strengthening muscles around the joints can provide stability, reducing the risk of injury or pain. Stretching is often not recommended for hypermobile joints, as it can worsen symptoms by overstretching the joints further. Instead, therapy focuses on controlled movements and building strength where muscles may be weaker than they should be.

Exercises and Treatment Options for HSD
Physical therapy treatment may include exercises that target muscle strength and joint stability, as well as using orthoses or braces to support unstable joints. Taping can also provide extra support, and therapists might recommend using ice or heat to manage discomfort. While manual therapies like massage can help reduce pain initially, the goal is often for patients to learn how to manage their symptoms independently and use physical therapy as needed.
Most physical therapists prefer to focus on one area of the body at a time, helping patients learn how to manage their symptoms without feeling overwhelmed. Over time, a physical therapist can help develop a safe, long-term exercise plan that promotes overall health, while also minimizing joint strain. This is particularly important for maintaining heart, lung, muscle, and joint health, as well as cognitive function.
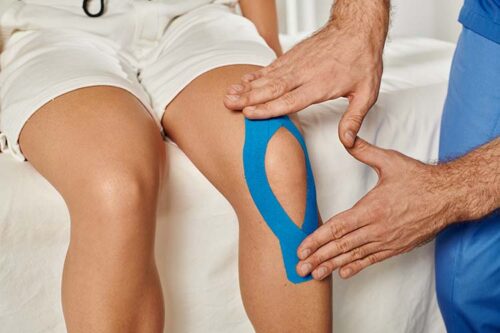
How to Stay Active and Healthy with HSD
Conclusion
Joint hypermobility and HSD can present unique challenges, but with the right management plan, individuals can live active and healthy lives. Physical therapy offers targeted strategies to stabilize joints, improve strength, and manage symptoms effectively, allowing people to participate in daily activities and exercise safely.
If you’re dealing with joint hypermobility or experiencing symptoms of Hypermobility Spectrum Disorder, reach out to our expert physical therapists for a personalized treatment plan.

Megan Bardach
PT, DPT
Orthopedic Therapist




